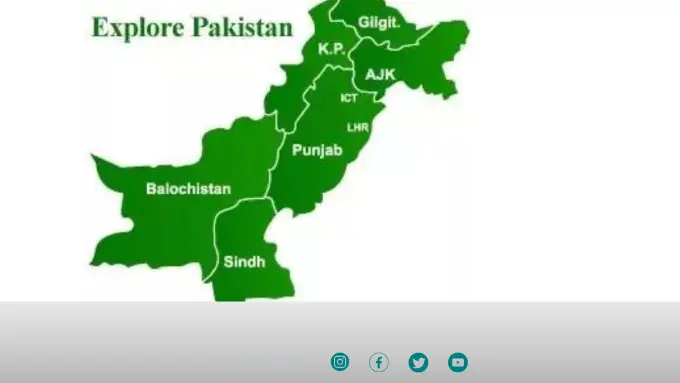
Pakistan’s administrative landscape is marked by its provincial divisions, each contributing to the country’s rich cultural tapestry and diverse identity. Understanding the number of provinces in Pakistan and their significance is essential for comprehending the country’s governance structure, cultural dynamics, and regional disparities. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the historical background, current provincial setup, significance of provincial autonomy, cultural richness, administrative and political dynamics, challenges and opportunities, and future outlook regarding Pakistan’s provincial divide.
Historical Background
The evolution of Pakistan’s provincial boundaries is deeply rooted in its historical journey. From the partition of British India in 1947 to subsequent constitutional developments, Pakistan’s provincial makeup has undergone significant changes. The impact of historical events, such as the One Unit Scheme in the 1950s and the subsequent restoration of provincial autonomy, has shaped Pakistan’s current provincial structure. Constitutional provisions related to provincial autonomy have played a crucial role in defining the relationship between the federal government and the provinces.
Current Provincial Setup
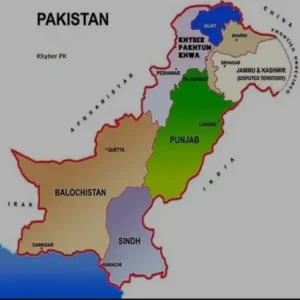
Pakistan is currently divided into four provinces: Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), and Balochistan. Each province boasts its own unique geography, population demographics, and cultural heritage. Punjab, the most populous province, is known for its fertile plains and historical significance. Sindh, home to the ancient civilization of Mohenjo-Daro, is characterized by its rich cultural heritage and diverse linguistic landscape. Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, located in the northwest, is known for its scenic beauty and cultural diversity. Balochistan, Pakistan’s largest province by area, is renowned for its rugged terrain and rich natural resources.
Significance of Provincial Autonomy
Provincial autonomy plays a crucial role in Pakistan’s governance structure, ensuring that provincial governments have the authority to manage their affairs independently. Key areas of provincial jurisdiction include education, healthcare, agriculture, and local government. However, challenges and controversies surrounding provincial autonomy, such as resource distribution and administrative capacity, persist and require careful consideration.
Provincial Diversity and Cultural Richness
Pakistan’s provinces are characterized by their diverse cultural landscapes, encompassing a myriad of languages, ethnicities, and traditions. Celebrating this cultural richness is essential for fostering unity and harmony across provinces. While linguistic and ethnic differences exist, Pakistanis take pride in their shared national identity and the diversity that defines their provincial heritage.
Administrative and Political Dynamics
Provincial governments play a significant role in Pakistan’s political landscape, with provincial assemblies and chief ministers overseeing local governance and policy implementation. The interplay between provincial and federal governments is crucial for maintaining a balance of power and ensuring effective governance across the country.
Challenges and Opportunities
Pakistan’s provinces face various challenges, including regional disparities, economic inequalities, and governance issues. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts to promote inclusive development, foster inter-provincial cooperation, and harness provincial resources for economic growth. However, with these challenges come opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and progress.
Future Outlook
The future of Pakistan’s provincial divide holds both challenges and opportunities. Potential changes to the provincial setup, such as the creation of new provinces or administrative reforms, may reshape the country’s governance structure. However, the overarching goal remains the same: to build a prosperous and harmonious Pakistan that embraces its diverse provincial identities while fostering national unity and stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pakistan’s provincial divide is a cornerstone of its identity and governance structure. Understanding the number of provinces in Pakistan and their significance is essential for navigating the country’s complex socio-political landscape. By embracing the diversity and cultural richness of its provinces, Pakistan can chart a path towards inclusive development, sustainable progress, and national unity. As Pakistan continues to evolve, its provinces will play a pivotal role in shaping its future trajectory and realizing its full potential as a multi-provincial nation.
Read more:how to earn money online in pakistan
FAQ’s
1. How many provinces are there in Pakistan, and what are their names?
Pakistan is currently divided into four provinces: Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), and Balochistan. Each province has its own unique geography, culture, and demographics, contributing to the country’s rich diversity.
2. What is the significance of provincial autonomy in Pakistan?
Provincial autonomy is crucial for Pakistan’s governance structure as it allows provincial governments to manage their affairs independently in key areas such as education, healthcare, and agriculture. This decentralization of power helps address local needs and ensures effective governance at the grassroots level.
3. How do Pakistan’s provinces contribute to the country’s cultural richness?
Pakistan’s provinces are characterized by their diverse cultural landscapes, encompassing a wide range of languages, ethnicities, and traditions. Celebrating this cultural richness fosters unity and harmony across provinces, reinforcing the shared national identity while embracing the diversity that defines Pakistan’s provincial heritage.