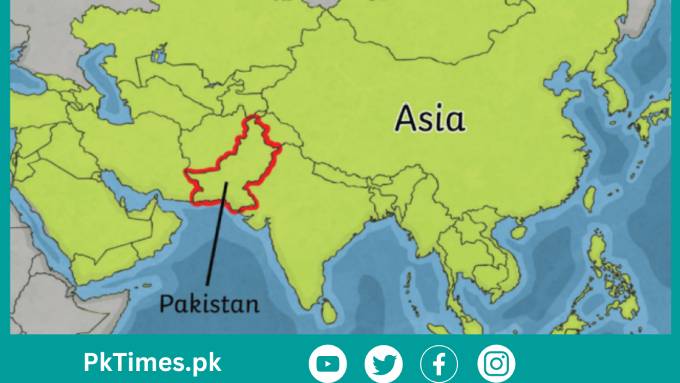
Where is Pakistan Located in Asia: Pakistan, a land of vibrant culture and diverse landscapes, holds a strategic position in the heart of South Asia. Its geographical location not only defines its boundaries but also plays a pivotal role in shaping its history, politics, and economy. Nestled in the western part of the Indian subcontinent, about Pakistan shares borders with several neighboring countries, including India, Afghanistan, Iran, and China. Its location at the crossroads of South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East makes it a key player in regional affairs.
Geographical Positioning of Pakistan
Subcontinent Location
Pakistan is situated in South Asia, commonly referred to as the Indian subcontinent. This subcontinent is defined by the Indian tectonic plate and encompasses countries like India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka.
Borders with Neighboring Countries
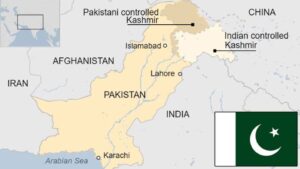
The country shares its eastern border with India, its western border with Afghanistan and Iran, and its northern border with China. To the south lies the Arabian Sea, providing Pakistan with access to important maritime trade routes.
Pakistan’s Role in South Asia
Pakistan’s location in South Asia positions it as a bridge between the Middle East, Central Asia, and the Indian Ocean region. This strategic position has influenced its history, as well as its cultural and economic ties with neighboring countries.
Historical Context of Pakistan’s Location
Partition from India
Pakistan’s creation in 1947, following the partition of British India, was influenced by its desire for a separate Muslim state. The partition led to the formation of two independent nations: India and Pakistan, with the latter comprising two geographically distinct regions, East and West Pakistan (now Bangladesh and Pakistan, respectively).
Creation of Bangladesh
In 1971, East Pakistan seceded from West Pakistan, leading to the formation of the independent nation of Bangladesh. This event further reshaped the geopolitical landscape of South Asia.
Pakistan’s Strategic Importance
Political and Economic Significance
Pakistan’s location grants it significant political and economic importance. It serves as a crucial transit route for trade between South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East. Additionally, its proximity to the Strait of Hormuz, a key oil shipping route, enhances its strategic value.
Influence on Regional Dynamics
Pakistan’s location influences regional dynamics, particularly in terms of security and geopolitics. Its relationships with neighboring countries, such as India, Afghanistan, and China, are shaped by historical tensions, territorial disputes, and geopolitical interests.
Pakistan’s Natural Features
Pakistan boasts diverse natural features, including mountain ranges like the Himalayas and the Karakoram, fertile plains, rivers like the Indus and the Ganges, and coastal areas along the Arabian Sea.
| atural Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mountain Ranges | Pakistan is home to several mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, the Karakoram Range, and the Hindu Kush. These majestic ranges not only define Pakistan’s landscape but also offer breathtaking views and opportunities for adventure tourism. |
| Rivers | The Indus River, often referred to as the lifeline of Pakistan, flows through the length of the country, providing water for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and sustenance to millions of people. Other significant rivers include the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, and Sutlej. |
| Coastal Areas | Pakistan has a coastline along the Arabian Sea, stretching over 1,000 kilometers. The coastal areas are characterized by sandy beaches, mangrove forests, and diverse marine life. They play a crucial role in trade, fishing, and tourism industries. |
Cultural Diversity in Pakistan
Pakistan is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions. Its diverse population includes Punjabis, Sindhis, Pashtuns, Baloch, and Urdu-speaking Muhajirs, among others. This cultural diversity is influenced by Pakistan’s historical interactions with various civilizations, including the Indus Valley civilization, Persian, Arab, and Central Asian cultures.
Impact of Location on Climate
Pakistan’s location influences its climate, which varies from arid to temperate and alpine. The country experiences four distinct seasons, with hot summers, mild winters, and monsoon rains in the summer months.
Economic Implications of Location
Pakistan’s strategic location has both economic advantages and challenges. While its position as a transit route enhances trade and commerce, geopolitical tensions and security concerns can disrupt regional connectivity and economic development.
Pakistan’s Relations with Neighboring Countries
Pakistan’s relationships with neighboring countries are multifaceted, influenced by historical, political, economic, and security factors.
| Neighboring Country | Description |
|---|---|
| India | Pakistan’s relationship with India is complex and often marked by tensions, stemming from historical conflicts, territorial disputes, and divergent political ideologies. Despite occasional attempts at reconciliation, issues like the Kashmir conflict continue to strain bilateral ties. |
| Afghanistan | Pakistan shares a porous border with Afghanistan, which has implications for security and stability in the region. While the two countries have historical and cultural ties, their relationship is influenced by issues like cross-border terrorism and refugee flows. |
| Iran | Pakistan’s relationship with Iran is characterized by economic cooperation, particularly in trade and energy sectors. However, differences over issues like border security and regional geopolitics occasionally strain bilateral ties. |
| China | Pakistan and China share a strong strategic partnership, exemplified by the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and close diplomatic ties. The relationship is anchored in mutual interests, including economic development, regional stability, and counterterrorism efforts. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pakistan’s location in South Asia is central to its identity and significance on the world stage. Its strategic position, diverse landscapes, and cultural heritage make it a country of immense importance, shaping regional dynamics and influencing global affairs.
Read More: when islamabad became capital of pakistan
FAQs
- Is Pakistan part of the Middle East?
- No, Pakistan is located in South Asia, not the Middle East. However, its proximity to the Middle East influences its politics and culture.
- What are the main geographical features of Pakistan?
- Pakistan is characterized by mountain ranges, rivers, plains, and coastal areas. The Himalayas, the Indus River, and the Arabian Sea are some of its prominent features.
- How does Pakistan’s location impact its climate?
- Pakistan’s climate varies from arid to temperate and alpine due to its diverse geography. Its proximity to the Arabian Sea and the Himalayas influences rainfall patterns and temperatures.
- What role does Pakistan play in regional politics?
- Pakistan’s strategic location and geopolitical importance contribute to its role as a key player in regional politics. It often mediates between neighboring countries and influences regional security dynamics.
- Why is Pakistan considered strategically important?
- Pakistan’s location at the crossroads of South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East gives it strategic significance. It serves as a vital transit route for trade and energy flows, impacting regional and global geopolitics.